In order to understand what Bitcoin is, we need to understand the technology it is built on; the blockchain.
Blockchain is to Bitcoin, what the internet is to email. A big electronic system, on top of which you can build applications. Currency can be considered one of them.
Blockchain technology
Blockchain technology has aroused a lot of interest and hopes in many different sectors. Following the crisis of 2008, the financial system lost the people’s trust and has shown some of its weak points, and worse, its potential downfall. It was during this period of mistrust toward financial institutions and governments that blockchain appeared. The first mention of blockchain emerged during the economic crisis in 2008, where Mr. Satochi Nakamoto created the Bitcoin, a peer-to-peer cash electronic system.
In a paper published in 2008 named “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System”, the revolutionary programmer stated that e-commerce was relying too much on third parties such as financial institutions for the process of electronic payment. He stated that even if “the system works well enough for most transactions, it still suffers from the inherent weaknesses of the trust-based model” (Nakamoto, 2008). His solution is an “electronic payment system based on cryptographic proof instead of trust, allowing any two willing parties to transact directly with each other without the need for a trusted third party. Transactions that are computationally impractical to reverse would protect sellers from fraud, and routine escrow mechanisms could easily be implemented to protect buyers.”
In other words, Mr. Nakamoto proposed a system that is ruled by “cold” technology that cannot be accused of partiality and in which we can trust, without limits or second thoughts.
How does blockchain works?
The main purpose of blockchain is to work as an online ledger that simplifies the way we transact monetary or non-monetary values. As our main interest is cryptocurrencies, we will talk about the functioning of the blockchain in this specific area and more specifically about Bitcoin.
On the technical side, the blockchain works as a public ledger that integrates all validated transactions in an endless list. This can be seen as a recorded history of all transactions since its creation in 2009, where each block represents transactions on a timeline basis of 10 minutes.
Transactions are validated by members of the blockchain that make sure that the transaction is valid. The verification of the transaction is called the proof of work. This is a complex mathematical problem that computers need to solve. Any transaction that is validated by the network community creates a block. This block contains 3 main pieces of information.
Firstly, the Data is the details of transactions; the “name” of the sender, the receiver, and the amount of the transaction.
Secondly, we have the hash, which can be compared to a fingerprint. A Hash is a cryptographic function that makes the links between blocks. Once a block is created, his hash is being calculated. If you change something inside the block, the hash will have to change which makes it very secure as if the hash changes it is no longer the same block.
The third element is the hash of the previous block. This makes the system very secure. If you attempt to alter the hash of a block, its hash will no longer match up with the hash of the next block which makes the system very hard, if not impossible, to break.
Moreover, each block that is completed is time-stamped, which avoids any risk of duplications. Once completed, the block is sent to the network and appended to the chain.
To conclude, in order to create a new block in the chain, we need to verify that the transaction is valid, solve a mathematical problem and get the right by consensus from other participants to insert this new block into the blockchain. This new technology has the potential to be a game-changer in today’s economy as it could make many trades and industries far more efficient and reliable.
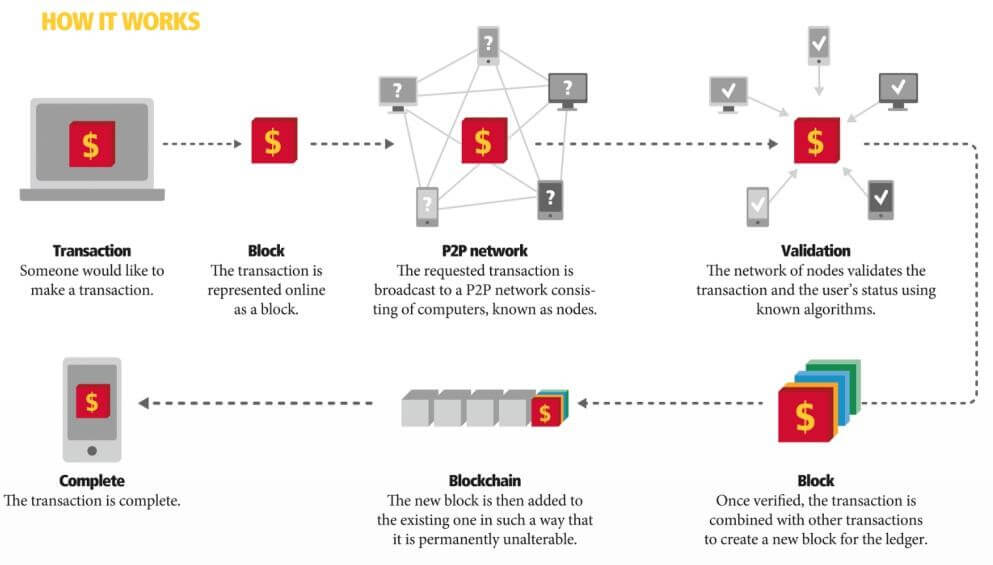
Source: http://www.delivered.dhl.com/content/dam/delivered/master/issues/2017-03/images/issue-3-17-p25-explained-blockchain- full.jpg