In today's dynamic financial markets, everyone has the liberty to select an asset class of their choice for investment or day trading. The power of choice ranges from traditional assets like Real Estate and Mutual Funds to more complex and high-end ones like Private Equity and Alternative Investment Strategies. Understanding Risk and Return in Different Asset Classes is pivotal to determining the profitability of investments. With this, we delve into the nitty-gritty of Real Estate Investment, a tangible asset class that has proven to be a reliable source of income across time.
Moving onto the realm of Investing in Mutual Funds, we aim to provide you insights into this popular choice of investment that allows diversification of risk. We then transition to the more exclusive field of Private Equity Investments, which could offer high returns albeit with higher risk. Furthermore, we explore Alternative Investment Strategies for those who wish to venture beyond traditional investment routes.
One crucial factor in investments is the Understanding of Asset Class Liquidity, it is the ease with which an investment can be converted into cash. We also delve into how various economic factors can impact these asset classes. To manage investment risks, understanding and Managing Asset Class Correlation is a necessity as it influences the volatility of your investment portfolio. With this comprehensive guide, we aim to equip you with a multi-dimensional understanding of asset classes and multi-asset trading platforms. Thus, enabling you to make well-informed decisions about your investment journey.
Contents: Major Asset Classes for Investing
- What is an asset class?
- Asset classes for diversification
- What are the 3 asset classes?
- What are the 5 major asset classes?
- What are the 7 asset classes?
- Understanding Risk and Return in Different Asset Classes
- Asset Allocation with FlowBank
- Investing in Stocks
- Fixed Income investing
- Forex trading
- Trading Indices
- Investing in ETFs
- Commodities trading
- Futures & Options trading
- Cryptocurrencies
- Real Estate Investment
- Investing in Mutual Funds
- Private Equity Investments
- Alternative Investment Strategies
- Understanding Asset Class Liquidity
- Impact of Economic Factors on Asset Classes
- Managing Asset Class Correlation
What is an asset class?
An asset class is a way to group financial assets that have similar qualities. For example, among currencies there is the US dollar (USD) and Swiss franc (CHF), among commodities there is gold and oil and among equities there is Amazon stock and Tesla shares.
Asset classes for diversification
Asset classes are one of the first considerations for how to invest. The idea is to have an asset allocation strategy that puts a certain percentage of your funds into each asset class. This provides asset class diversification because each asset class behaves differently under different market conditions.
Most of the time there is little correlation, and even negative correlation between different asset classes. Portfolio managers use this information to create diversified portfolios that can survive in bull and bear markets. Furthermore, these asset classes can help an investor get exposure to a fund structure under one relationship. Most global funds are traditional funds and a few of them such as hedge funds are alternative investments.
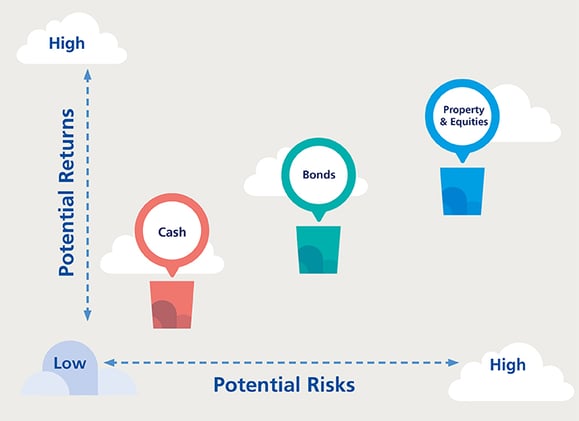
What are the 3 asset classes?
The starting point for all investing are these three assets. For those preferring a very hands-off approach, there will probably be little need to go much beyond these three for ways to store your money. All of which are very liquid and offer risk diversification, from cash investments, which are safest and offers lowest returns to stocks, which are risky but have historically offered the best long-term returns.
The main components of the stock market include large cap, inflation rates, absolute returns and market cap.
- Cash
- Equities
- Bonds
What are the 5 major asset classes?
Expanding on the main three, property and commodities might also be included into the asset class categories.
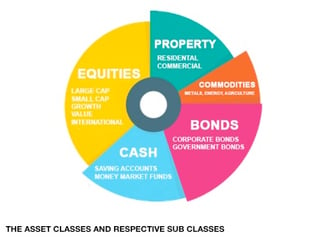
Commodities are very speculative and tend to require expert knowlege, while property is an excellent addition to any portfolio, offering reliable income-earning and capital gains potential, but has higher barriers to entry and is more illiquid. For most investors, these five types of assets will make up the bulk of their long-term portfolio.
- Stocks (equities)
- Bonds (fixed-income)
- Property
- Commodities
- Cash
What are the 7 asset classes?
As you might be starting to realise, there is more than one way to slice a cake. Different investors split assets up into different classes, depending on their needs for a diversifed investment portfolio. Another classic way to seperate asset classes is as follows:
- Domestic Equities
- Global Equities
- Currency
- Bond/Fixed Income
- Commodities
- Real Estate
Understanding Risk and Return in Different Asset Classes
Asset classes are distinct types of investments that behave similarly under market conditions. They have their own unique risk and return characteristics. The four main types of asset classes are equities (stocks), fixed income (bonds), money market instruments, and real estate.
- Equities: These are high-risk investments, but they also provide high returns. Their performance is primarily influenced by the financial health of the company and the overall economic climate.
- Fixed income: These are lower-risk investments compared to equities. They offer fixed returns, making them suitable for conservative investors.
- Money market instruments: These are very low-risk investments. They offer modest returns and are highly liquid.
- Real estate: This asset class can be risky depending on the location and market conditions, but it can also provide high returns. Real estate investments include commercial properties, residential properties, and real estate investment trusts (REITs).
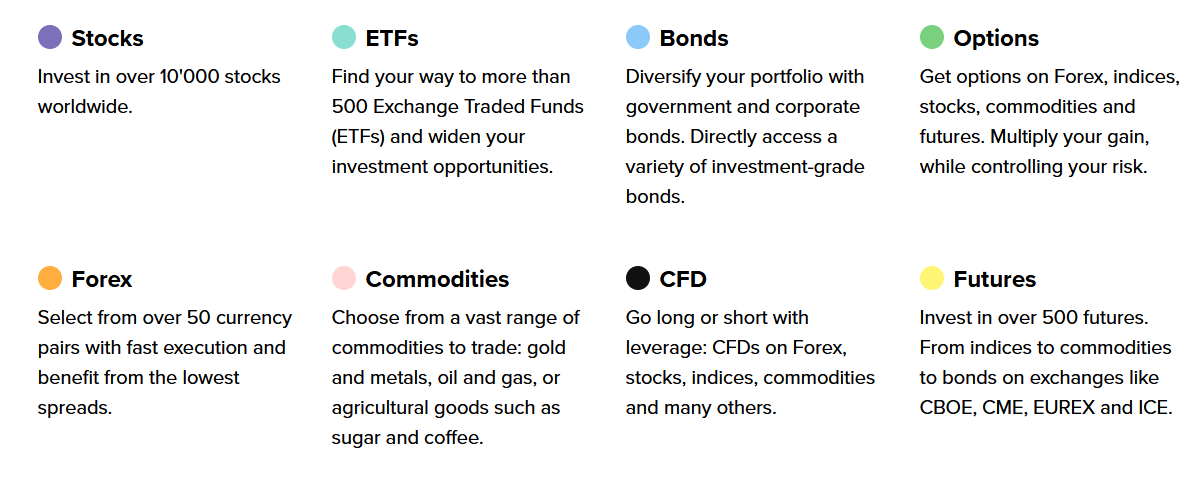
Asset Allocation with FlowBank
FlowBank has the modern, well-informed digital customer in mind, when offering eight asset classes, as well as cash deposits to create the ideal asset allocation portfolio, all in a smartphone app or on your desktop computer.
Investing in Stocks
Also called equities, stocks are cash flow producing entities, a business, that generate value over time, and that are listed on a public stock exchange like the London Stock Exchange.
A companie issues shares of stock in the company. Each share is a contract of ownership in a fraction of a company’s business. Public markets are great in that anybody can become part owner of a company. Some famous companies like IKEA are not tradeable on an exchange because they are not public companies. Private companies like IKEA may become public companies after filing for an initial public offering, and companies that are already public like Tesla, may become private once again. Within this asset class, there are sub categories of stocks like blue chips firms and small caps.
Fixed Income investing
Fixed income means an income that is recurring over time. ‘’Fixed’’ refers to a pre-set periodic payment and ‘’income’’ means revenue. The concept behind fixed income securities is simple; lend your money to a business or government in return for periodic interest payments. A good example would be money market instruments such as federal agency notes and treasury bills.
Money has a price because a dollar today could be used to finance many projects that could grow tomorrow. Tomorrow, your $1 dollar invested could be $2 dollars if that project grows so if you lend your money, you would like to be paid for its use.
Enter ‘’Bonds’’. Imagine a piece of paper from the government (or a digital copy of that paper) that says that if you lend them $1,000 today, they will pay you $25 every month for three years and that at the end of the three years you will get your $1,000 back.
Fixed income. Recurring income over fixed time periods until the bond hits its ‘’maturity date’’. These bonds and other assets such as index funds and money market funds, or obligations can be short term, or medium term, or very long term. This is also called a debt market, a market where a lot of promises to pay back others are monetized and traded and this market is larger than the equities market.
Forex trading
Forex is an abbreviation for ‘’Foreign Exchange’’ meaning a marketplace where investors can buy and sell currencies. You can buy American Dollars with your currency and then sell it in return for another currency and so on and so forth with all available currencies.
This is a huge market, and the biggest in terms of trading volume. The point behind trading currencies is that currencies have values that go up and down depending on many economic factors. Such factors include, changes in a country’s money supply, trade dynamics between countries, and demand for a specific currency to earn interest. The Forex market is open all day long five times a week. The goal behind forex is to make profits on price differences between currencies over time.
Trading Indices
If you have heard of the S&P500 you have a sense of what an index is. An index is a broad signal of the performance of a conglomerate of stocks.

The S&P500 is composed of 500 companies and this is a way for market participants to gauge the current stock market climate. There are a variety of indexes that focus on different sectors such as the Russell 2000 Index whose main focus are small cap stock (companies with small market capitalizations).
The famous Dow Jones Industrial Average is used as a proxy to determine the general health of the U.S. economy, and this is what radios allude to when talking about ‘’the markets’’. You need to know this for trading because it will come in handy as a ruler when trading exchange traded funds who often times try to ‘’beat’’ the market index return.
Investing in ETFs
An exchange traded fund (ETF) is a publicly traded fund that invests in a basket of companies that you can buy and sell shares of ETFs just like you would a regular stock.
An ETF will buy many different stocks and build a portfolio of companies. Some ETFs focus on a specific industry, some are domestic ETFs others international. There exists a broad variety of ETFs an example being the SPDR S&P 500 ETF (SPY) and ETFs that tracks the S&P500. ETFs contain all sorts of securities like stocks and bonds and commodities.
Commodities trading
Commodities are things like grains, gold, beef, and oil. These are the everyday basic goods used in households, and by industry.

Commodities are known to move in an uncorrelated way to stocks which is a good way to diversify a portfolio. Commodities are more stable with respect to market volatility but they generate lower returns on investment. Commodities can be traded through ETFs where a fund manager while by the commodity and hold it in a trust or more commonly through a futures contract (next section).
Futures & Options trading
Options are contracts where an investor pays for the opportunity but not the obligation to buy or sell an asset at a specific price.
There are two types of options, puts and calls. Calls allow you to buy the asset. Puts allow you to sell the asset at the contract agreement date and strike price. If a stock is falling and you have the ability to sell (put) your option at a high price, you win. If the stock is going up and you exercise the right to buy at a lower price, you win. The point is that you pay money to have the opportunity to either sell or buy a stock a predetermined price for a specific duration of time.
Futures are different. They were designed originally for the producers of the commodity as a hedging tool against changes to prices due to things like the weather. Nowadays, most trading is done by speculators (traders). A futures contract enables someone to buy a commodity at a pre-specified price with the option to take delivery at that price at the end of the contract (typically 3-months).
Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies are different from cash and cash equivalents. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum are tradable digital assets that are traded on exchanges through a platform such as Coinbase. They are also traded through exchange traded products like ETNs. You can also trade public companies that mine bitcoin.
No matter how many investment assets you feel you can spare, it is wise to understand how the market works and invest accordingly.

Real Estate Investment
Real estate investment involves buying, owning, managing, renting, or selling real estate for profit. It's a popular investment option due to the potential for high returns and the stability of the asset. There are multiple ways to invest in real estate:
- Direct ownership: You can purchase residential or commercial properties directly. You can then earn income by renting out the property or selling it at a profit.
- Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs): These are companies that own and manage income-generating properties. You can invest in a REIT by buying shares, just like in a regular company.
- Real estate funds: These are mutual funds that invest in real estate companies and REITs. They offer the benefit of diversification because they invest in a variety of properties.
Investing in Mutual Funds
Mutual funds are an ideal investment option for those who want diversification and professional management of their investments. They pool money from multiple investors to buy a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other assets. The main types of mutual funds are:
- Equity funds: These funds invest primarily in stocks. They may focus on a specific sector, such as technology or healthcare, or a specific geographic region.
- Bond funds: These funds invest in bonds and other debt securities. They aim to provide regular income to investors.
- Money market funds: These funds invest in short-term, high-quality debt securities. They are considered low-risk investments.
- Balanced or hybrid funds: These funds invest in a mix of stocks and bonds to balance risk and return.
Private Equity Investments
Private equity involves investing in private companies or buying out public companies to make them private. Private equity funds typically require a significant minimum investment and are mostly accessible to institutional investors or high-net-worth individuals. The two main types of private equity are:
- Leveraged buyouts (LBOs): These involve buying a company using a significant amount of borrowed money. The assets of the company being acquired are often used as collateral for the loan.
- Venture capital: This type of private equity involves investing in start-ups or small companies with high growth potential. Venture capital investments are risky but can offer high returns if the company is successful.
Alternative Investment Strategies
Alternative investment strategies refer to non-traditional methods used to achieve potential returns. These may include hedge funds, real estate, private equity, commodities, and more. Unlike traditional strategies, alternative investment strategies can offer higher returns and diversification benefits, but they also come with their own unique risks.
- Hedge funds: These are usually only accessible to accredited investors and use a range of strategies like short selling and leveraging to generate high returns.
- Real estate: This involves investing in property, either directly or through Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs).
- Private equity: This involves investing in non-publicly traded companies or buying out public companies to take them private.
- Commodities: These are physical assets like gold, oil, agricultural products, etc.
Understanding Asset Class Liquidity
Asset class liquidity refers to the ease with which an asset can be bought or sold without impacting its price. Cash and cash equivalents are considered the most liquid assets as they can be easily converted into other forms. On the other hand, assets like real estate or private equity are considered less liquid as they take longer to sell and may require significant price reductions.
Factors affecting asset class liquidity include:
- Market conditions: In volatile market conditions, liquidity can decrease as fewer buyers may be willing to purchase the asset at its current price.
- Asset type: Some assets are inherently more liquid than others. For example, stocks and bonds are generally more liquid than real estate or art.
- Economic factors: Economic downturns can lead to decreased liquidity as investors may shy away from riskier assets.
Impact of Economic Factors on Asset Classes
Economic factors can significantly impact the performance of various asset classes. For instance, interest rates, inflation, economic growth, and political stability can all affect the value of your investments.
- Interest rates: When interest rates rise, bond prices typically fall. Conversely, when interest rates fall, bond prices usually rise.
- Inflation: Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money over time, which can impact the real return of your investments.
- Economic growth: Strong economic growth can boost corporate profits, leading to higher stock prices. However, rapid growth can also lead to inflation and higher interest rates.
- Political stability: Political instability can increase uncertainty, leading to higher volatility in financial markets.
Managing Asset Class Correlation
Asset class correlation refers to how different asset classes move in relation to each other. When two asset classes are positively correlated, they tend to move in the same direction. If they're negatively correlated, they move in opposite directions. Diversification involves combining asset classes with low correlation to reduce risk.
Strategies for managing asset class correlation include:
- Diversification: By investing in a variety of asset classes, you can reduce the risk that poor performance in one area will significantly impact your overall portfolio.
- Rebalancing: This involves periodically reviewing and adjusting your portfolio to maintain your desired asset allocation.
- Asset allocation: This is the process of dividing your investment portfolio among different asset classes based on your investment goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon.





